The driving principles for data architecture have drastically changed. This is why most of the practices we used to leverage in the past are no longer valid.
Architectures are based on principles; if you change the principles, you also need to change the architectures. Conway's law makes this very clear, and people ignoring this aspect will end up undermining their data practice implementation and their organization's goals.
It is impossible to continue using several centralized practices in a market where the communication structure and the ownership model are moving towards decentralization.
In this article, we will deep-dive into data product orchestration and scheduling. Orchestrating a chain of interconnected data products in a decentralized environment can be challenging. Traditional waterfall and top-down scheduling approaches are ineffective in such scenarios.
Event-based reactive scheduling mechanisms are a far better alternative to address this. This article explores the importance of event-based scheduling in a distributed ownership environment where no one can be fully accountable for an end-to-end data pipeline.
Avoiding the complexity and ownership challenge
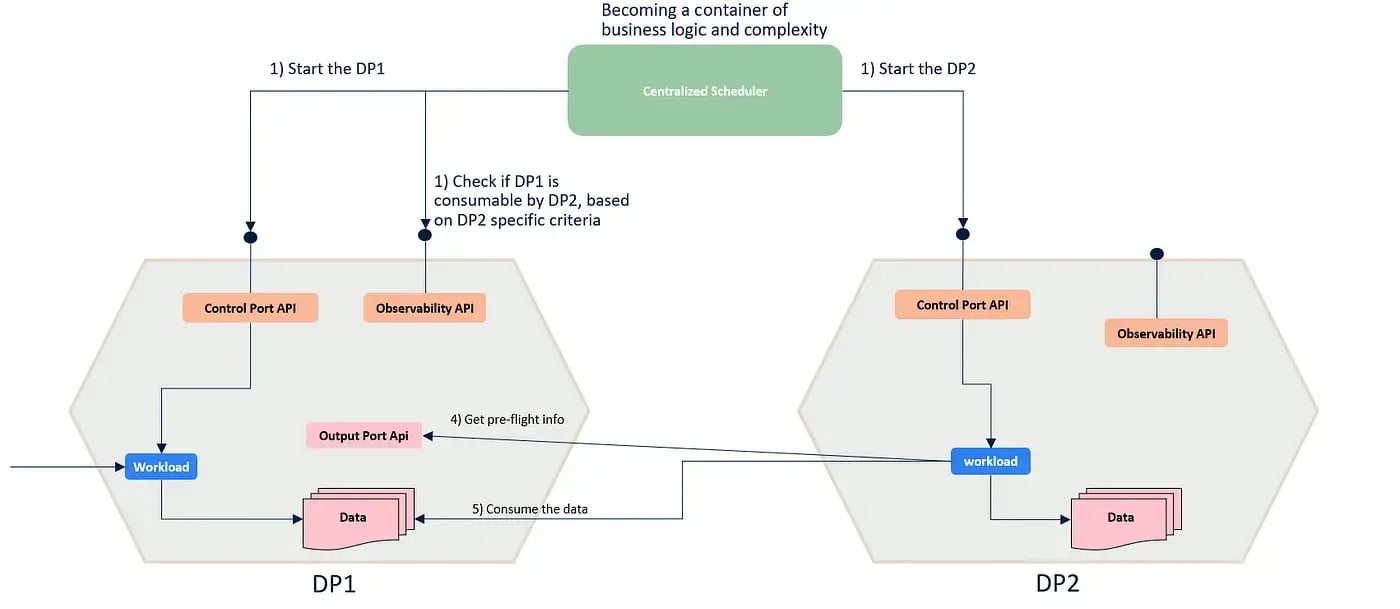
In the traditional centralized and top-down scheduling mechanisms, we rely on some scheduling platform (e.g., Control-M) where we accumulate all the configurations, timings, scheduling logic, and dependencies among the data pipelines.
When the scheduling logic becomes more intricate, it poses challenges for ownership and maintenance. Who manages the interdependencies?
Without considering the business process needs first, it's impossible to decide if and when to schedule something. In a centralized organization, this could be feasible and effective, but in a decentralized environment, who will take care of this complexity?
The following image represents how not to orchestrate data products.
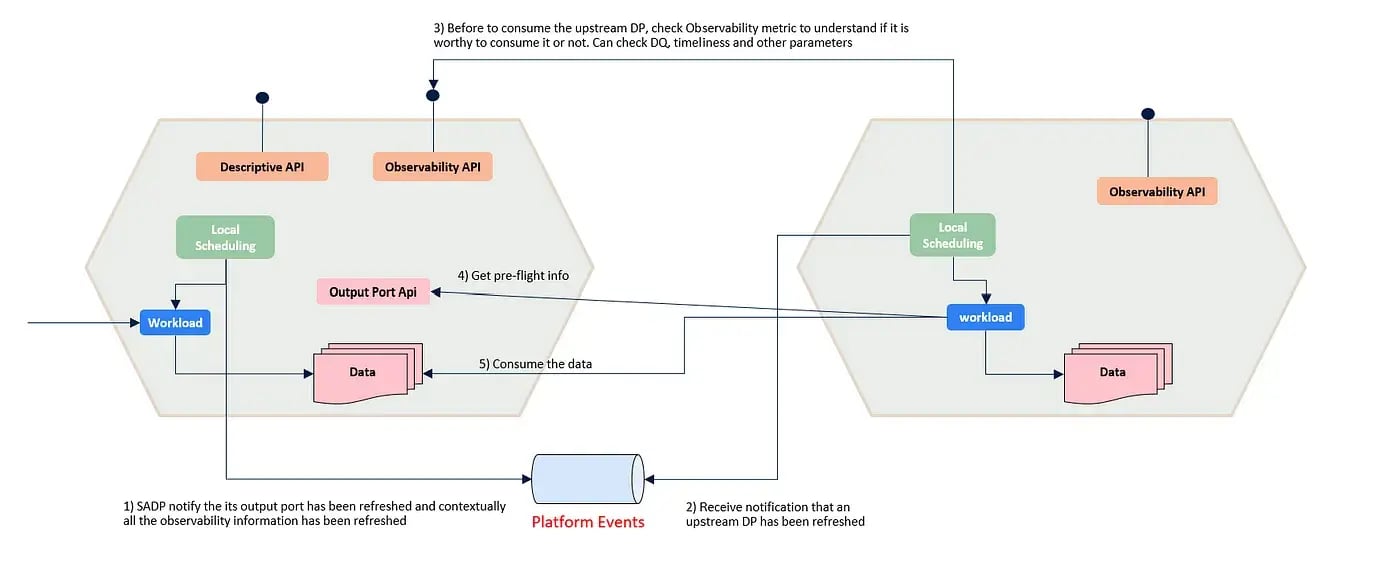
Event-based reactive scheduling:
In a decentralized environment, where multiple data products interact, scheduling processes in a top-down manner becomes impractical.
Event-based reactive scheduling provides a solution by triggering data product workloads based on events published on a platform event bus. This event-driven approach enables data products to react to changes in the upstream processes, ensuring a seamless flow of data across the chain.
Event-based reactive scheduling offers greater agility and flexibility by decoupling dependencies and reducing inter-process complexities.
A standard for publishing events must be enforced to ensure consistency and interoperability across the data product ecosystem. Computational policies can be established to define the structure and content of events, effectively forming a data contract.
This contract acts as a guarantee between the data product publisher and the consumers, promoting reliable data exchange and reducing integration issues.
Adhering to the enforced standard allows all consumers to react to events uniformly, simplifying the integration process and enhancing the overall data product orchestration.
In this pattern, the full logic to decide if, when, and how to start the data consumption from another data product is in the downstream data product (which is consuming the data).
This increases the complexity of the Data Product but assigns it clear ownership, concentrating the full business logic in one single place where the business knowledge resides.
By adopting an event-driven approach, ownership is distributed among the relevant data products, reducing the burden on central IT teams. This shift promotes more transparent accountability and empowers stakeholders to take ownership of their respective steps, leading to increased reliability and streamlined data product orchestration.
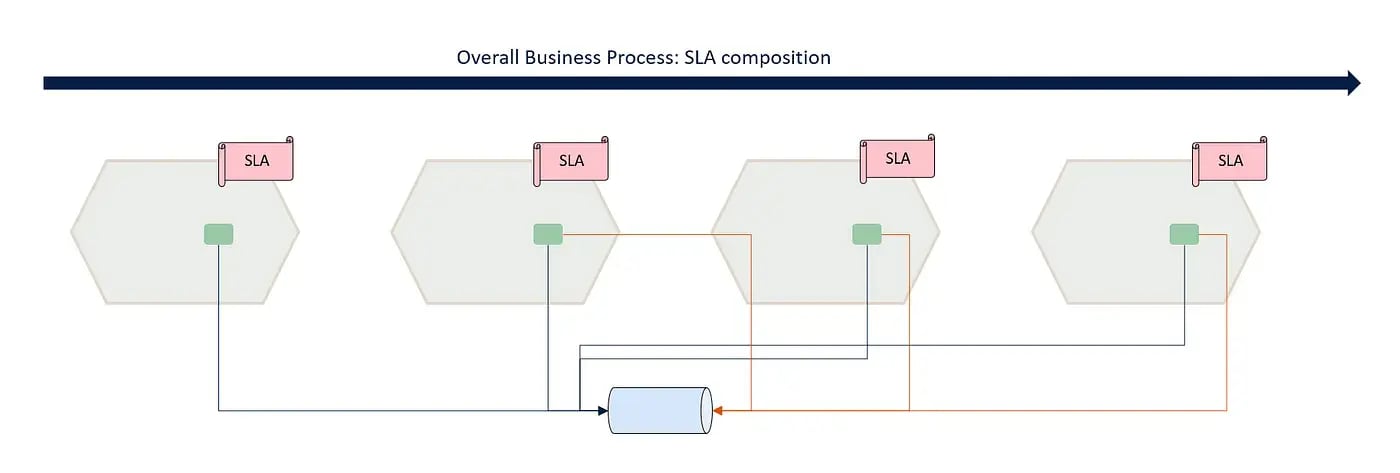
Cascading SLA mechanism:
Service level agreements (SLAs) play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and performance of data products.
In event-based orchestration, the SLA becomes a cascading mechanism, where the end-to-end process depends on the SLAs declared and respected by each involved data product. By summing up the individual SLAs, organizations can have a holistic view of the overall performance and make informed decisions about data product dependencies. This cascading SLA mechanism helps maintain accountability and transparency throughout the data product chain.
This is especially important in all those business processes with external constraints (e.g., regulatory cut-offs ).
Observability and runtime policies:
Manading data product orchestration, observability, and runtime policies is essential. Observability provides real-time insights into the performance and health of data products, allowing organizations to identify and address issues promptly.
Runtime policies trigger alerts to notify downstream processes and data consumers when an upstream data product fails to meet its declared SLA. This proactive approach enables consumers to assess the current state of the upstream data product before consuming its data.
By evaluating compliance with the data contract, data consumers can make informed decisions regarding data consumption and implement appropriate retry strategies to meet their SLAs.
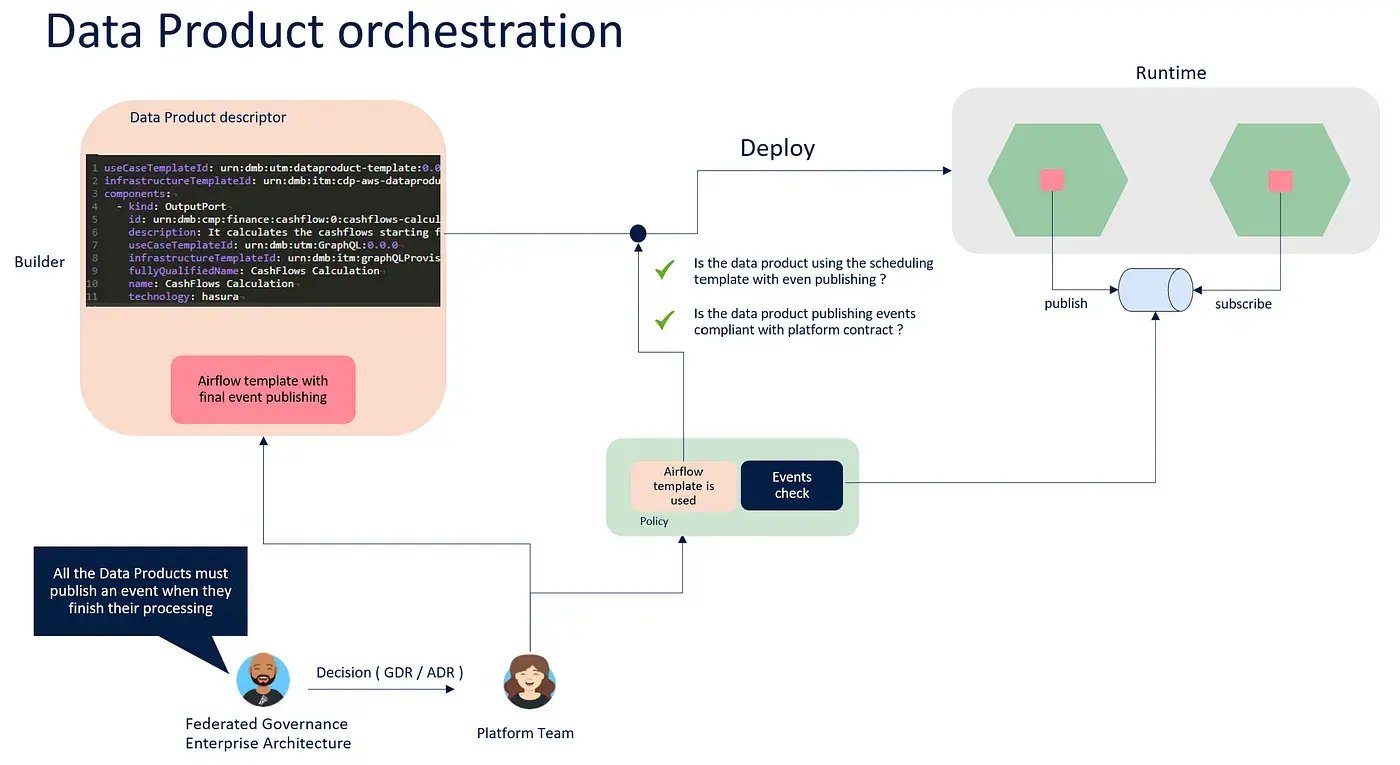
To introduce this pattern in your data practice, you need the following components:
- Platform Event Bus: Data Producers publish events based on their activity and where Data Consumers subscribe to what they are interested in and react to those events. It is an essential decoupling element between producers and consumers to avoid monolithic scheduling chains.
- Local Scheduling template: To help Data Product teams to implement the publishing and the subscribing logic in conformity with platform requirements, it is important to provide a working example of it. The platform team should create a template with such behaviour to facilitate the implementation.
- Computational policies: The pub/sub mechanism represents a contract between users and the platform itself. It is crucial to enforce this contract with computational policies, ensuring that events are published, correct and compliant with the SLA. A Data Product must embed this mechanism to achieve interoperability.
- Observability API Template: In such a decentralized environment, the data consumer must have all the information to understand whether it is worth consuming the upstream DP, applying its business logic. To enable this, all the data products should expose Observability information ( through the API ) to let the consumer make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Data product orchestration in a decentralized environment requires a shift towards event-based reactive scheduling. Organizations can establish a seamless data flow across interconnected processes by leveraging an event-driven, technology and platform-agnostic approach.
Adhering to an enforced standard and data contracts ensures consistency and interoperability, while a cascading SLA mechanism maintains performance and accountability. Observability and runtime policies are vital in proactively addressing SLA breaches and enabling data consumers to make informed decisions.
By avoiding complexity and ownership challenges, organizations can achieve efficient data product orchestration and drive impactful insights for their business operations.